Introduction
Many compounds and polluted environment could classified as Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated in biological systems by aerobic metabolism and also by exogenous sources such as drugs, UV light, ionizing radiation and pollution systems [1]. Major deleterious effects are caused by hydroxyl radical (OH. ) generated from H2O2 as considered predominant in ROS group and by the superoxide (O2- ) species generated in the presence of redox active transition metals [2]. Sies [3] focused on redox signaling under physiological conditions, where higher concentrations (>100 nM) lead to adaptive stress responses and damage of biomolecules. Endogenous and exogenous defence mechanisms such as antioxidant enzymes and non-enzymatic antioxidant compounds are available in living organisms could limit the levels of ROS and their biological damage [4].
Lopez-Lazaro [5] explained the possible relevance of hydrogen peroxide to cancer. He linked the increase in cellular levels to DNA alterations, cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance. Key indicators of oxidative stress (lipid peroxidation measured by malondialdehyde MDA) have been shown to increase immediately after heavy training in the plasma [6]. Plasma MDA levels continued to be elevated 24 h after severe exercises in the non-vitamin supplemented subjects.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) has been in clinical practice for several decades. It has been used for the treatment of numerous disorders such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) intoxication, ischemia-reperfusion cardiac injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, heavy metal toxicity, and chemotherapy-induced toxicity [7]. It works by increasing glutathione levels and binding with the toxic breakdown products of paracetamol. The acetylated precursor of L-cysteine has relatively low toxicity, where 30% of the drug is cleared by renal excretion [8]. Below 5% NAC is thought to be associated with its N-deacetylation in the intestinal mucosa and first pass metabolism in the liver [9]. It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.
Epidemiological studies have strongly suggested that diet rich in fruits, vegetables and cereals play a crucial role in the prevention of chronic diseases and certain type of cancer by quenching free radicals [10]. The beneficial health effects are mainly due to the presence of antioxidants such as polyphenols, carotenoids and anthocyanins. Recently, Okoko and Ere investigated that Carica papaya leaf extract possessed antioxidant and free radical scavenging ability through reducing H2O2 induced erythrocyte haemolysis and lipid peroxidation comparing to ascorbic acid [11].
Moreover, Ajila and Rao examined mango peel extract as inhibited agent against oxidative hemolysis of rat erythrocytes by H2O2 [12]. It was found that lovastatin as a cholesterol lowering drug had antioxidant property against H2O2 induced oxidative stress in rats [13]. Our study investigates the importance of some dried neutrient fruits such as golden berry or husk tomato, nabk and sycomore facing the oxidative stress produced from hydrogen peroxide. These local fruits need to be under light to declear their importance as natural antioxidants. Data in our study were compared with the standard valuable N-acetyl cysteine to measure the potential importance for intoxicated rats.
Methods
Body weight gain BWG, and feed Efficiency ratio FER were determined in the biological experiment using the following equation [14];
BWG=(Final weight – Initial weight) / experimental days
FER=Daily body weight gain (g)/Daily food consuming (g) × 100
Hydrogen peroxide H2O2 was purchased from United Company for Chem. Med. Prepn., and N-Acetyl cystein was purchased from SEDICO drug industrial company.
Biological experiment Fourty two female Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing 120 ± 5 g were purchased from Research Institute of Ophthalmology, Giza, Egypt. Animals were given two weeks acclimation period, during which they were fed ad libitum a standard rat chow diet [15], with alternated 12-h dark/light cycle, and the ambient temperature was held between 21- 25°C. All studies were performed in accordance with the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, as adopted and promulgated by research Institute of Ophthalmology, Giza on 2015.
Plant materials; three fruits were bought and prepared from Zaitone, Cairo - Egyptian market, washed with distilled water to remove any impurities and air dried. Minded dried fruits were mechanical grinded and used for further studies. Fruits were used in the biological experiment as follows; Husk tomato or golden berry (Physalis pubescens L.; family Physalis), Nabk (Rhamnus sp.; family Rhamnaceae) and Sycomore (Ficus sycomorus; family Moraceae).
Animals were divided into six groups (7 rats each), as follow;
Group (1) normal control group were fed with standard rat chow diet. Group (2) rats were fed the chow diet and 100 mg H2O2 /kg body weight daily in drinking water to induce stress. As been mentioned in literature, LD50 for hydrogen peroxide is 2000 mg/kg (oral for mouse). Group (3) rats fed allowed standard diet and administered oral NAC (100 mg/ kg bw) allowed before drinking H2O2in water. Group (4) rats fed with standard diet mixed with dried Husk powder (200 mg/kg bw) (Hs) daily and allowed drinking H2O2 in water. Group (5) rats fed with standard diet mixed with dried Nabk (200 mg/kg bw) (Nb) daily and allowed drinking H2O2 in water. Group (6) rats fed with standard diet mixed with dried Syco more (200 mg/kg bw) (Sy) daily and allowed drinking H2O2 in water. The used concentrations were expected from related research.
Assessment of Activity Biological parameters such as food consumption was monitored daily and body weight was determined once a week. After the experimental period (five weeks), food was forbidden for 12 hours. The fasting rats were sacrificed and blood samples were collected into clean centrifuge tubes. Blood samples were allowed to coagulate and centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 20 minutes to separate blood serum. Separated serum was stored at -20°C for subsequent biochemical analyses.
Biochemical Analysis The determination of serum creatinine was performed according to [16]. Serum alkaline phosphatase enzyme ALP was measured with colorimetric method [17]. ALP and creatinine were measured to prove the liver and kidney dysfunction, respectively. Plasma lipid peroxide (Malondialdehyde, MDA) was determined [18]. The antioxidant marker enzyme catalase CAT was measured in plasma by using heparin anticoagulant [19]. MDA and CAT were considered as oxidative stress markers. Plasma was freeze at -80°C and the assessment was done in days. The activity was defined as the micromoles of H2O2 decrease per milligram of protein per minute.
Histopathological study Autopsy samples were taken from the rats in different experimental groups. In 10% formal saline solution, samples were fixed for twenty four hours. Washing was done in tap water then serial dilutions of absolute ethyl alcohol were used for dehydration. After that, specimens were cleared in xylene and embedded in paraffin at 56°C in a hot air oven for twenty four hours. Paraffin bees wax tissue blocks were prepared for sectioning at 4 microns thickness by slidge microtome. The obtained tissue sections were collected on glass slides, deparaffinized and stained by hematoxylin and eosin stain for histopathological examination through the light microscope [20].
Statistical analysis Using Statistical package for social sciences SPSS program [21] means were calculated among 7 replicates, with their Standard Deviations (± SD) for each group. Analysis of variance was applied to make statistical comparisons (ANOVA) with Dennett’s post hoc test in between 5% probability
Results
Data proved that H2O2 dramatically decreased compared to control group the body weight and food efficiency ratio significantly through the experiment (Table 1). While, data showed that husk tomato followed by NAC groups improved the induction caused by H2O2 intoxication.
| Groups |
BWG (g)
Mean ± SD |
FER Mean ± SD |
ALP(IU/l) |
Creatinine (mg/dl) |
| control |
72.6 ± 9.711a |
12.96 ± 4.554a |
113.29 ± 27.19c |
9.00 ± 2.83a |
| H2O2 |
54.75 ± 3.961b |
9.776 ± 3.804b |
229.13 ± 30.60a |
9.33 ± 2.16a |
| H2O2+NAC |
73.4 ± 7.603a |
13.10 ± 5.013a |
107.95 ± 18.59c |
6.33 ± 2.86b |
H2O2+Hs
|
76.2 ± 12.133a |
13.607 ± 6.663a |
163.71 ± 69.81b |
7.33 ± 2.16a |
H2O2 +Nb
|
64 ± 3.464ab |
11.42 ± 4.321ab |
156.49 ± 32.63b |
7.00 ± 1.22a |
H2O2 +Sy
|
70.6 ± 13.334a |
12.607 ± 66.671a |
131.13 ± 48.48b |
9.67 ± 3.89a |
| F |
3.73 |
3.73 |
5.798 |
1.382 |
| Sig. |
0.012** |
0.012** |
0.001 |
0.266 |
Table1: Effect of Hydrogen peroxide toxication and protective groups in
body weight gain (BWG g), food efficiency ratio (FER), alkaline phosphatase
(IU/l) and creatinine (mg/dl)
The values are the [mean ± SD] of 7 rats in each group.
Alkaline phosphatase ALP as indicator for liver dysfunction mechanism showed dramatic increase with H2O2 treatment compared to control group. NAC showed superior significant improvement according to intoxicated hydrogen peroxide treated group followed by syco more additives for rat diet for ALP activity. On the other hand, creatinine in the kidney profile showed insignificant increase value for hydrogen peroxide induction, and NAC was the most significant reliever among the tested groups. More than 52% and 32% reduction in ALP and creatinine values, respectively has been fulfilled by treating rats with NAC orally (Table 1).
CAT and GPx could neutralize peroxides from oxidative stress into water and oxygen as been mentioned [22]. CAT was measured through H2O2 produced colorimetrical and the changes in CAT values were due to inducing by H2O2 administration in drinking water. From our results, increasing MDA oxidative stress marker directly influence in decreasing CAT enzyme values. Hydrogen peroxide treatment alone significantly reduced the CAT value as common antioxidant enzyme in correlation data with significant high MDA proxidation indicator score for the oxidative stress role (Table 2). CAT is found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen. Also, catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes. Husk tomato followed by sycomore or nabk proved to fail in reliving the oxidative stress effects in MDA and CAT values, respectively. That was clear from the insignificant data compared with the infected hydrogen peroxide group and the treated H2O2 /NAC group as well.
| Groups |
CAT(ᵤM H2O2 /min/ mg protein)
|
MDA (nmol/g tissue) |
| control |
493.18 ± 272.43a |
5.65 ± 1.17b |
| H2O2 |
303.27 ± 87.47b |
12.51 ± 4.84a |
H2O2 +NAC
|
574.28 ± 239.53a |
6.94 ± 2.01b |
H2O2 + Hs
|
487.93 ± 126.08ab |
10.34 ± 4.10ab |
H2O2 + Nb
|
470.65 ± 290.24ab |
12.14 ± 0.93a |
H2O2 +Sy
|
335.55 ± 165.19b |
10.81 ± 6.75ab |
| F |
1.206 |
5.47 |
| Sig. |
0.336 |
0.002 |
Table 2: Effect of hydrogen peroxide and protective groups in antioxidant parameters as catalase enzyme CAT (ᵤM H2O2 /min/mg protein) and malondialdehyde MDA (nmol/g tissue)
The values are [mean ± SD] of 7 rats in each group
Liver sections of rats treated with hydrogen peroxide showed dilatation, congestion of hepatic sinusoids and congestion of hepatoportal blood vessel with portal oedema (Figure 1a). Dilatation of hepatic sinusoids also has been detected comparing to normal hepatic lobule structure (Figure 1b). Hydropic degeneration of some hepatocytes has been found when treated female rats with H2O2 accompanied with NAC oral injection (Figure 1c). On the other hand, Husk supplemented in diet enhanced the H2O2 effects with no histopathological changes (Figure 1d). In the same while, slight kupffer cells activation has been found with H2O2 and Nabk fruits (Figure 1e). Sycomore supplemented in diet with H2O2 treatment showed slight vacuolations of hepatocytes (Figure 1f).
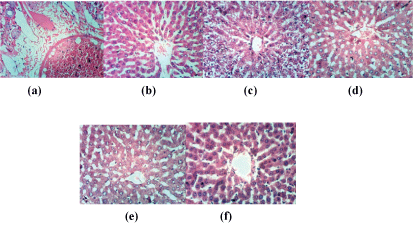
Figure 1: liver sections of rat from control group (a); liver section of rat treated with H2O2 (b) liver section of rat treated with H2O2 and NAC (c); with H2O2 and Husk fruits (d); with H2O2 and Nabk fruits (e); with H2O2 and Sycomore fruits (f) (H and E X 400)
Secondly, kidney sections of rat from group control were showing normal histological structure of renal parenchyma (Figure 2a). Kidney sections of rat from group H2O2showed atrophy of glomerular tuft, distension of Bowman’s space and focal renal haemorrhage (Figure 2b). NAC protected the effects of H2O2 by showing normal histopathological pattern (Figure 2c). Slight vacuolation of epithelial lining renal tubules has been found with husk fruits as protective agents against oxidative stress (Figure 2d). Nabk supplemented fruits for group treated with H2O2 showed atrophy of some glomerular tuft (Figure 2e). On the other hand, sycamore showed slight vacuolation of endothelial lining glomerular tuft (Figure 2f).
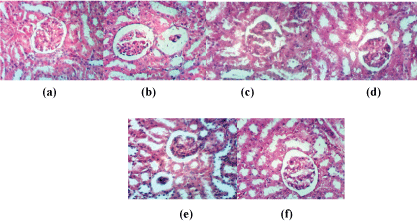
Figure 2: Kidney sections of rat from control group (a); kidney section of rat treated with H2O2 (b); kidney section of rat treated with H2O2 and NAC (c); H2O2 and Husk fruits (d); H2O2 and Nabk (e); H2O2 and Sycomore fruits (f) (H and E X 400)
Brain rat sections of control (Figure 3a) illustrated no histopathological changes. While, brain sections of rat from group H2O2 showed necrosis of neurons & cellular oedema and perivascular oedema (Figures 3b and 3c) illustrated brain section of rat from group H2O2+ NAC showing necrosis of neurons. In rat brain, it was found that converted NAC is subsequently de-acetylated to Cys and supposed to be slowly released from the cells into the blood [8]. Brain sections of rat from group Husk showed no histopathological changes (Figure 3d) and neuronophagia of necrotic neurons occurred with fresh nabk (Figure 3e). Moreover, Figure (3f) showed that group Sycomore has cellular oedema.
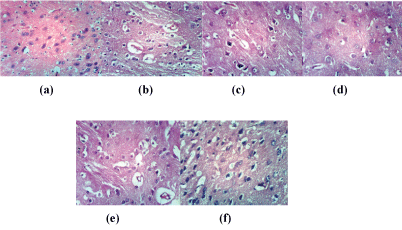
Figure 3: Brain sections of rat from control group (a); (14a,b) section of rat treated with H2O2 (b); Brain section of rat from group H2O2 +NAC (c); group Husk (d) sections of rat from group Nabk (e) group Sycomore (f) (H and E X 400)
Discussion
NAC– among the tested groups- was the most potent factor in quenching the oxidative stress effect caused by H2O2 . Although NAC doesn’t react with O2 or NO, it reacts with highly oxidizing radicals such as OH. produced from hydrogen peroxide and.NO2 from NO and can also bind redox-active metal ions [7]. The fruits and leaves of husk tomato (Physalis species) represented an important source of antioxidants, antiinflammatory, antiseptic and anticancer substances, mainly due to the presence pf physalines and withanolides [23]. NAC was introduced in the clinical practice for a large number of reported studies [8]. Orally administered NAC is rapidly absorbed but also undergo extended first-pass hepatic metabolism thus resulting in low bioavailability [24]. Supplementation of Cys or Cys-containing drugs as NAC may be a feasible way to increase intracellular Cys levels thus boosting GSH synthesis. Effects of NAC are supposed to exert by NAC or its metabolites Cys and GSH, However, abundant metabolism of NAC and Cys to inorganic sulfate and taurine, and its oxidized form in plasma to its symmetric disulfide NAC-NAC.
On the other side, Giustarini et al. [9] mentioned the role of high doses of NAC used in paracetamol intoxication. NAC infusion has been widely used in acute hepatic failure but convincing evidence of NAC’s benefit is lacking [25]. Salla et al. [26] have recently investigated the phytochemical protection from oxidation caused by free radicals. Data agreed with our results where inducing oxidative stress lowered SOD, CAT, GPx activities and GSH levels in oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide in HepG2 cells. Oxidative stress, first described [27] showed severe effects on liver, kidney and brain sections.
Recent research agreed to our data, Kang et al. stated that traditional herb medicine has therapeutic efficacy against H2O2 [28]. Hydrogen peroxide caused a reduction in cell viability by increasing the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species, leading to DNA damage and apoptosis. The phenology of husk tomato cultivated in Mexico and the nutritional potential have been recorded and proved by [29]. They studied good candidate’s species for breeding and developed husk species as new crops of nutritional quality. In closed and recent protective study [30], vitamin E had a significant effect in improving the repair potential of mesenchymal stem cells to counteract H2O2 induced oxidative stress in vitro.
Research explained that cancer cells produce high amounts of H2O2 [5], and in the same while there is evidence that H2O2 can induce apoptosis in cancer cells as well. The dual role of H2O2 may make cancer cells more susceptible to H2O2 induced cell death than normal cells. Low levels of reactive oxygen species in general can be beneficial, while excessive accumulation can promote cancer. Research provides evidence from the chemical and histpathological tests that some discovered nutraceuticals are highly effective in eliminating or decreasing cancer cells.
Article Information
Article Type: Research Article
Citation: Shaker ES, Mnaa S (2017) Protective Effect of Some Local Plants against Oxidative Stress Caused By Hydrogen Peroxide. J Environ Sci Toxicol Stu 1(1): doi http://dx.doi.org/10.16966/2576-6430.104
Copyright: © 2017 Shaker ES, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Publication history:
Received date: 23 Feb 2017
Accepted date: 14 Sep 2017
Published date: 19 Sep 2017




